

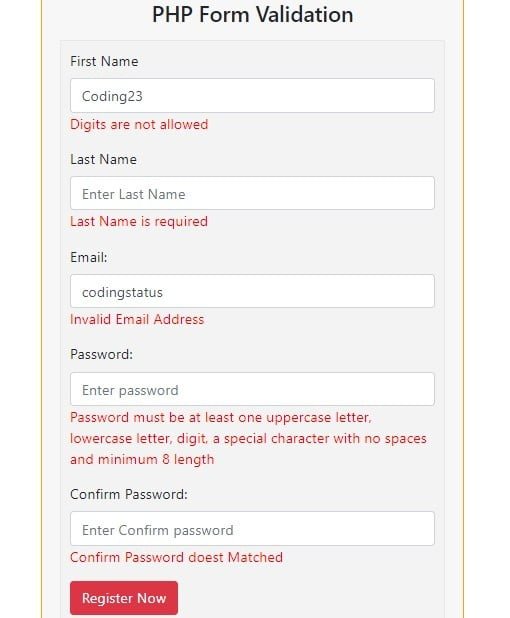
If there are form errors, then the form should be redisplayed to the user and be pre-populated with the recently submitted data.
#Isset php form submit code#
More complex code could be written which would highlight each input field that has an error. Listing all errors above the form is the easiest approach. = "Please fix the following errors:" $output. Here is a code example which will take an array of errors and output them as a list inside a div for display on the form page. If something goes wrong during form processing, then the error needs to be communicated to the user so they can fix the data and try again. This has the advantage of making it easy to redisplay the form again if there are errors and to re-populate its input fields with the recently submitted values. The second request for the page (POST, when the form is submitted) will process the form. The first request for the page (GET, when the URL is entered) shows the form. HTML inputs without names are not included in the form data.Īnother common form-processing technique is for a form to submit back to its own page. Note that name="submit" is optional for the form to work, but required for this technique to work. The second technique is to put a name/value pair on the submit input and then detect if there is a value set for $_POST. This can be packaged up as an easy-to-remember function. The first technique is to check the value of REQUEST_METHOD. There are two techniques to detect when a form has been submitted. Ī common form-processing technique is to have a page which responds differently depending on whether a form has been submitted to it. PHP 7 added a new null coalesce operator ( ?) to make it even shorter and easier. The boolean ? true\_result : false\_result syntax is called a ternary operator and is handy for writing an if-else statement on one line. It is a good practice to make sure that values are set for variables before using them, and to set default values if they are not set. Those values can be accessed using their key names. PHP automatically assigns the form data to the associative array in superglobal $_POST. PHP is helpful for processing form values. Anyone who can see the request will see the POST data in plaintext. We don't see POST data in the URL like we do with GET data, and POST data does not need to be encoded or decoded like GET data does.Įven though POST data is not as prominently visible, do not be fooled into thinking they are private. The values will be packaged up and sent as "POST data". This form will submit the values of its input fields to "register.php" using the request method "POST".


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
